Eczema is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it’s commonly associated with dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, the symptoms and causes of eczema can be surprisingly diverse and unexpected. From sudden flare-ups in previously clear skin to unusual triggers exacerbating symptoms, there’s much to learn about this complex condition.
Whether you’re dealing with it yourself or simply curious about this common skin disorder, this blog post will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the unexpected symptoms, causes, and treatments of it. So, get ready to explore the lesser-known aspects of this condition and gain a better understanding of how to manage it for clearer, healthier skin.
What Is Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. It can affect people of all ages, but it most commonly develops in childhood and persists into adulthood. The exact cause of it is not fully understood, but it’s believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It can be triggered by various factors such as irritants, allergens, stress, and temperature changes. There is currently no cure for it, but it can be managed with treatments such as moisturizers, topical steroids, and immunomodulators.
Eczema Symptoms
Dry, Itchy Skin
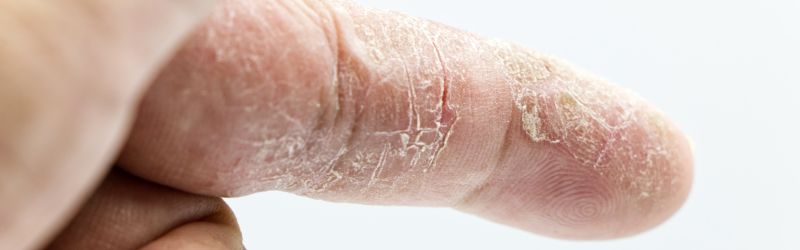
One of the most common symptoms of it is dry, itchy skin. This may start as a mild irritation but can quickly become more intense and uncomfortable. The itching sensation can be so severe that it can interfere with sleep and daily activities, making it difficult to focus or complete tasks.
Red Or Inflamed Patches
Eczema often presents as red or inflamed patches of skin. These patches may appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, hands, and feet. The affected skin may be rough, scaly, or even cracked in severe cases.
Blisters Or Oozing
In some cases, eczema can cause the skin to blister or ooze. This symptom may occur in response to an irritant or an allergic reaction. Blisters may be small or large and can be filled with clear or yellow fluid. Oozing may occur when the blisters burst, leaving behind a wet, weepy surface.
Thickened Or Leathery Skin
Chronic eczema can cause the skin to thicken or become leathery in texture. This symptom, known as lichenification, is caused by constant scratching or rubbing of the affected area. Thickened skin can be especially difficult to treat and may require more aggressive interventions.
Changes In Skin Color
Eczema can cause changes in skin color, such as darkening or lightening. These changes may occur in response to inflammation or as a result of prolonged scratching and rubbing. In some cases, the affected skin may also become hyperpigmented, meaning it appears darker than the surrounding skin.
Causes Of Eczema
Genetics
Eczema often runs in families, and studies suggest that genetic factors play a role in its development. People with a family history of it, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop it themselves.
Allergens
Eczema is often triggered by exposure to allergens, which can include pet dander, dust mites, pollen, mold, or certain foods. These allergens can cause the immune system to overreact, leading to inflammation and itching.
Irritants
Exposure to irritants such as harsh soaps, detergents, cleaning products, or fabrics can damage the skin barrier, leading to dryness and inflammation. This can trigger or worsen the symptoms in some people.
Stress
The stress can trigger eczema flare-ups in some people by altering the immune system’s response. It can also cause a person to scratch or rub their skin more, leading to further irritation.
Weather
Changes in weather conditions, particularly cold and dry weather in the winter, can cause the skin to become dry and itchy. Similarly, hot and humid weather in the summer can cause sweating, which can irritate the skin.
Hormones
Hormonal changes can affect the skin and trigger flare-ups, particularly in women. Fluctuations in estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause can cause symptoms to worsen. Some women may also develop eczema for the first time during pregnancy or menopause due to hormonal changes.
Best Treatments For Eczema
Moisturizers
Moisturizing the skin is an essential part of managing eczema. Regular application of moisturizers helps to hydrate the skin and maintain its barrier function, reducing dryness and itchiness. Look for fragrance-free and hypoallergenic moisturizers that contain ingredients like ceramides, glycerin, or hyaluronic acid, which help to lock in moisture.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed for the treatment, especially during flare-ups. These medications reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and help to improve the skin’s condition. They come in various strengths, and your doctor will determine the appropriate potency based on the severity and location of your eczema.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
Another class of topical medications used for eczema treatment is calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus. These medications help reduce inflammation and itching without the side effects commonly associated with corticosteroids. They are often recommended for sensitive areas like the face or skin folds.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines can be helpful in managing the itching associated with eczema. They work by blocking histamine receptors, which are involved in the itch response. Non-drowsy antihistamines are preferred during the day, while sedating antihistamines may be beneficial for relieving itching and promoting sleep at night.
Wet Wrap Therapy
Wet wrap therapy involves applying a moisturizer or topical medication to the skin, followed by wrapping the affected areas with wet bandages or clothing. This technique helps to hydrate the skin, enhance the absorption of medications, and reduce inflammation. It is often used during severe flare-ups or when other treatments are not providing adequate relief.
It’s important to note that eczema treatments may vary depending on the individual, the severity of the condition, and other factors. Consulting with a dermatologist or healthcare professional is crucial for proper diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan.
What Doctors Say About Eczema
Doctors recognize it as a chronic skin condition that affects many people worldwide. It is a complex condition that can be difficult to manage, and treatment options may vary depending on the severity and type of it. Dermatologists and other healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of maintaining good skin hygiene, avoiding triggers, and following a personalized treatment plan to manage symptoms effectively. They also emphasize the need for ongoing care and monitoring to prevent complications and ensure the best possible outcome for people with it.
FAQs
Can eczema be cured?
Eczema is a chronic condition, meaning there is no known cure. However, it can be effectively managed with proper treatment and self-care measures. By following a consistent skincare routine, avoiding triggers, and using prescribed medications, individuals can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that suits your specific needs and provides long-term management of it.
Is eczema contagious?
No, it is not contagious. It is not caused by a virus or bacteria and cannot be spread from person to person through direct contact. It is primarily a result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors. However, in some cases, it flare-ups can be triggered or worsened by certain infections or allergens, so it’s important to maintain good hygiene and avoid potential irritants.
Can eczema be prevented?
While eczema cannot be completely prevented, there are measures that can help reduce the risk of developing the condition or minimize flare-ups. It is recommended to moisturize the skin regularly, especially after bathing, to keep the skin hydrated and maintain its protective barrier. Identifying and avoiding triggers such as specific allergens, irritants, or certain fabrics can also help prevent flare-ups. Additionally, managing stress levels, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following a balanced diet may contribute to overall skin health and potentially reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms.

